AI Assistant
NetXMS includes an integrated AI assistant that helps with network monitoring, incident analysis, log investigation, and day-to-day administration tasks. The AI assistant connects to large language models (LLMs) and uses a set of built-in functions to query live NetXMS data, execute actions, and provide context-aware recommendations.
This chapter covers the configuration of LLM providers, the use of the AI assistant in the management client and command-line interface, background AI tasks, and the AI message system.
Getting Started
This section walks you through the minimal steps needed to enable the AI assistant and have your first conversation.
Prerequisites
A running NetXMS server (version 6.0 or later).
Access to at least one LLM provider: a cloud API (OpenAI, Anthropic) or a local Ollama instance.
An API key or token for the chosen provider (not required for Ollama with default settings).
At least one server module that provides AI skills and functions. The
aitoolsmodule is included in the open-source edition. Load it by addingModule=aitoolsto thenetxmsd.conf(before any named section).
Step 1: Configure an LLM Provider
Add a provider section to the server configuration file (netxmsd.conf).
The example below configures an OpenAI-compatible provider:
Module=aitools
[AI/Provider/openai]
Type = openai
URL = https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions
Model = gpt-4o
Token = sk-your-api-key-here
Slots = default
Restart the NetXMS server after changing the configuration file.
Note
The AI assistant is only available when at least one provider is configured.
If no provider has the default slot, the server will not start the AI
subsystem.
Step 2: Open the AI Chat
In the management client:
Switch to the Tools perspective.
Open the AI Assistant tool.
Type a message in the input field at the bottom and press Enter.
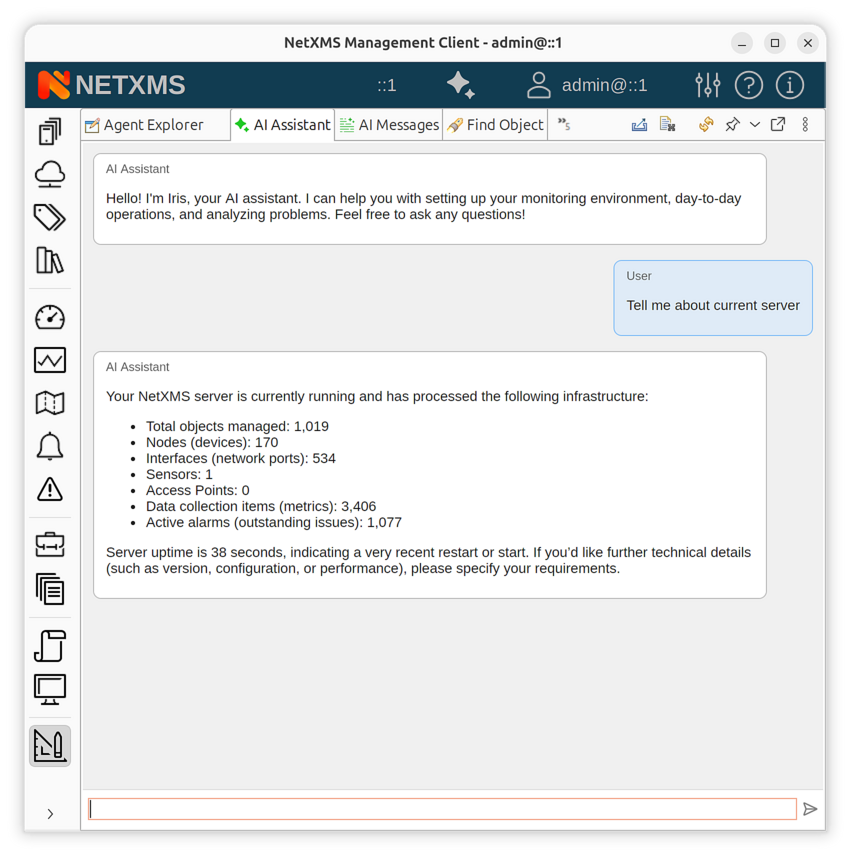
AI Assistant chat view in the management client
The AI assistant will respond using the configured LLM and may call internal functions to retrieve live data from the server (e.g., alarm lists, object details, historical metrics).
Step 3: Ask a Question
Try a simple query to verify the setup:
What are the current active alarms?
The AI assistant will use the alarm-list function to retrieve real-time
alarm data from the server and present the results. Function calls are
displayed in the chat as progress indicators so you can see what data is being
accessed.
How-to Guides
How to Configure LLM Providers
Providers are configured in the netxmsd.conf file under [AI/Provider/<name>]
sections. Each provider has a unique name and maps to one or more slots.
OpenAI-compatible provider
Works with the OpenAI API and any compatible service (Azure OpenAI, vLLM, LiteLLM, etc.):
[AI/Provider/openai]
Type = openai
URL = https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions
Model = gpt-4o
Token = sk-your-api-key-here
Temperature = 0.7
ContextSize = 128000
Timeout = 180
Slots = default,interactive
Anthropic provider
Connects to the Anthropic Messages API:
[AI/Provider/anthropic]
Type = anthropic
URL = https://api.anthropic.com/v1/messages
Model = claude-sonnet-4-20250514
Token = sk-ant-your-key-here
Slots = default,analytical
Ollama provider (local)
Runs models locally using Ollama. No API key is required for local deployments:
[AI/Provider/local-llama]
Type = ollama
URL = http://127.0.0.1:11434/api/chat
Model = llama3.2
ContextSize = 32768
Slots = fast
How to Use Provider Slots
Slots allow you to route different types of AI requests to different providers. For example, you can use a fast local model for quick responses and a more capable cloud model for deep analysis.
Assign slots to providers using the Slots parameter (comma-separated list):
[AI/Provider/gpt4]
Type = openai
Model = gpt-4o
Token = sk-your-key
Slots = default,analytical
[AI/Provider/local-fast]
Type = ollama
Model = mistral
Slots = fast
At least one provider must be assigned to the default slot for the AI
subsystem to initialize. See Provider slots for the complete list of
available slot names.
You can optionally set the global default provider explicitly:
[AI]
DefaultProvider = gpt4
How to Set Up AI Incident Analysis
The AI assistant can automatically analyze incidents when they are created from event processing rules.
Open Event Processing Policy in the Configuration perspective.
Edit the rule that creates incidents.
In the rule actions, enable one or more AI options:
AI Analyze Incident – triggers automatic incident analysis by the AI assistant.
AI Auto-assign – lets the AI assistant suggest and assign the incident to the most appropriate user based on past data and object responsibility.
Request AI Comment – adds an AI-generated analytical comment to the incident.
Select the analysis depth:
Quick – fast, high-level summary.
Standard – balanced analysis with root cause suggestions.
Thorough – deep analysis including topology context, event correlation, and historical incidents.
Optionally, enter a custom AI prompt to guide the analysis (e.g., “Focus on network connectivity issues” or “Check for recurring patterns over the last 7 days”).
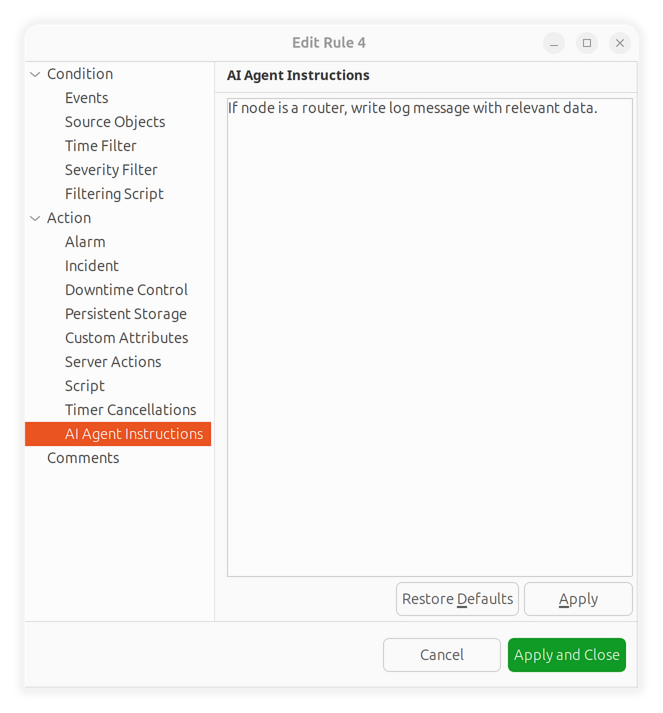
Event processing rule with AI analysis options
How to Create Background AI Tasks
Background tasks allow the AI assistant to work autonomously without user interaction. Tasks can run once or iterate over multiple executions, preserving state between runs.
From the chat interface:
Ask the AI assistant to create a task:
Create a background task to check the health of all core routers
every hour and notify me if any anomalies are found.
The AI assistant will use the register-ai-task function to schedule the task.
From the management client:
Open the Configuration perspective.
Navigate to AI Tasks.
Click Create new task.
Enter a description and the prompt (instructions for the AI assistant).
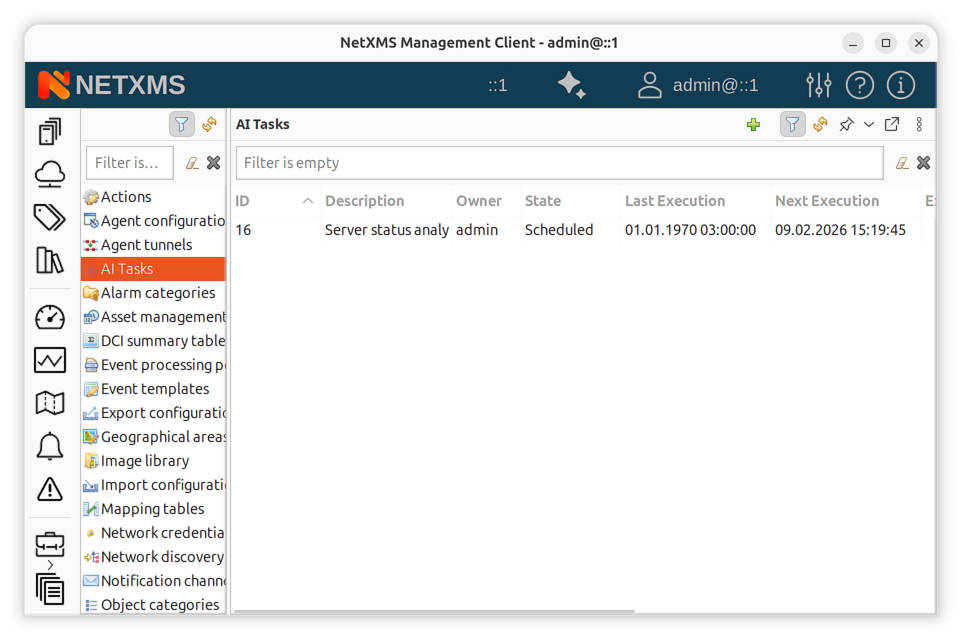
AI task manager in the Configuration perspective
Tasks appear in the task manager with their current state: Scheduled, Running, Completed, or Failed. The Explanation column shows a summary of what the task accomplished or why it failed.
How to Work with AI Messages
Background AI tasks communicate results through messages. Messages appear in the AI Messages panel in the Tools perspective.
There are three message types:
Informational – findings, reports, and status updates.
Alert – anomalies or warnings that require attention.
Approval Request – proposed actions that require user approval before execution.
To handle messages:
Open AI Messages in the Tools perspective.
Select a message to view its content in the detail panel.
For approval requests, click Approve or Reject.
Messages are automatically marked as read after 30 seconds. Expired messages (default expiration: 7 days) are cleaned up by the server.
How to Use the Command-Line Client
NetXMS provides nxai, a command-line interface for chatting with
the AI assistant from a terminal. The tool is included in the NetXMS
source tree under src/client/nxai and can be installed with pip:
pip install /path/to/netxms/src/client/nxai
Basic usage:
nxai --server netxms.example.com --user admin
With context binding:
# Bind to a specific node
nxai --server netxms.example.com --user admin --node web-server-01
# Bind to an incident
nxai --server netxms.example.com --user admin --incident 456
Connection parameters can also be set via environment variables:
NETXMS_SERVER, NETXMS_USER, NETXMS_PASSWORD.
Slash commands available during a chat session:
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Show available commands |
|
Exit the chat (aliases: |
|
Clear chat history |
|
Set object context for the conversation |
|
Set incident context |
|
Show current session information |
How to Export a Conversation
In the management client, right-click in the chat view and select Export Conversation. The conversation is saved as a Markdown file that includes all messages and function call summaries.
Concepts
Architecture Overview
The AI subsystem consists of the following components:
LLM Providers connect the NetXMS server to language models. Each provider is configured with a model, API endpoint, and authentication credentials. Multiple providers can be active simultaneously.
Provider Slots route AI requests to appropriate providers. Different slots
(e.g., default, fast, analytical) can point to different providers,
allowing you to balance cost, speed, and capability.
Functions are the bridge between the AI assistant and NetXMS data. When the AI assistant needs to access live information (alarms, objects, metrics, logs), it calls registered functions that execute on the server and return results. Over 50 functions are available covering alarms, incidents, objects, data collection, logs, SNMP, event processing, and more.
Skills are domain-specific instruction sets that the AI assistant loads on demand. Each skill includes a specialized prompt and a set of related functions. Skills are loaded dynamically during a chat session when the AI assistant determines they are needed.
Background Tasks allow the AI assistant to work autonomously. Tasks can run once or iterate with a configurable delay, preserving state between executions through a memento mechanism.
AI Messages are the output channel for background tasks. Tasks can post informational findings, alerts, or approval requests that users review in the management client.
Skills
Skills extend the AI assistant with domain-specific knowledge and capabilities. Each skill includes a detailed prompt with instructions and reference data, plus a set of functions for data access.
Note
Skills and functions are provided by server modules. The aitools
module, available in the open-source edition, provides the base set of
skills and functions listed below. Additional skills can be provided by
other modules, including enterprise and third-party ones. Load a module
by adding Module=<name> to the netxmsd.conf (before any named
section).
Available skills:
Skill |
Description |
|---|---|
Incident Analysis |
Root cause analysis, alarm correlation, incident history, topology context, and assignment recommendations. |
Log Analysis |
Search and correlate syslog, Windows events, SNMP traps, and NetXMS system events. Includes pattern detection and burst analysis. |
Data Collection |
Metric creation, threshold management, historical data analysis. Supports SNMP, agent, and script-based data origins. |
Event Processing |
Event template and processing policy management. Event flow analysis and action configuration. |
Inventory |
Hardware components, software packages, and network interface inventory. Integration with SNMP, WMI, and agent sources. |
Maintenance |
Maintenance mode scheduling and management. Alert suppression during maintenance windows. |
NXSL Scripting EE |
Compile, execute, and manage NXSL scripts. Includes script library browsing and ad-hoc script execution. |
Asset Management EE |
Track physical assets, manage properties, link assets to monitored objects, and audit change history. |
File Management EE |
Remote file operations on nodes with NetXMS agent: read, write, delete, rename, and integrity verification. |
Network Topology EE |
IP and MAC address location, network peer discovery, and route tracing between nodes. |
Scheduler Management EE |
Create and manage scheduled tasks for automated maintenance, script execution, and discovery operations. |
SSH Command Execution EE |
Secure remote command execution on servers and network devices with intelligent command classification and approval workflow. |
Note
Skills marked with EE require the NetXMS Enterprise Edition.
They are provided by the aiext and aissh server modules which are
only loaded when a valid Enterprise Edition license is present.
The AI assistant loads skills automatically based on the conversation context. You can also request a specific skill explicitly:
Load the log analysis skill and search syslog for authentication
failures in the last 24 hours.
Enterprise Skills
The following skills are available exclusively in the NetXMS Enterprise
Edition. They are loaded from the aiext and aissh server modules and
require a valid Enterprise Edition license.
NXSL Scripting
The NXSL scripting skill allows the AI assistant to compile, execute, and manage NXSL (NetXMS Scripting Language) scripts. It supports both ad-hoc script execution and working with the server script library.
The AI assistant can:
Compile NXSL scripts to check for syntax errors before execution.
Execute arbitrary NXSL scripts on the server.
Run existing scripts from the script library.
Browse and inspect scripts stored in the library.
This skill is useful for automation, custom data processing, and extending NetXMS behavior through scripting. For example, you can ask the AI assistant to write and run a script that checks the status of all nodes in a container or computes a derived metric from multiple data sources.
Asset Management
The asset management skill provides the AI assistant with the ability to track physical assets, manage their properties, and link them to monitored objects.
The AI assistant can:
List and search assets by name, serial number, MAC address, or any custom property.
View complete asset details and individual property values.
Set, update, and delete asset properties with schema validation.
Link and unlink assets to monitored objects (nodes, sensors, access points, mobile devices, chassis, and racks).
Inspect the asset attribute schema including data types, constraints, and enumeration values.
Review the full change log for compliance auditing.
When an asset is linked to a monitored object, properties marked for auto-fill (such as IP address, MAC address, vendor, and model) are automatically populated from the linked object.
File Management
The file management skill enables remote file operations on nodes that have the NetXMS agent installed.
The AI assistant can:
List directory contents on remote nodes.
Read text files (up to 1 MB).
Write and overwrite text files (up to 1 MB).
Delete files and directories.
Create directories.
Get file metadata including MD5 and SHA256 checksums.
Rename files.
All operations respect the agent’s FileStore root folder configuration and
enforce user access rights. Different permissions are required for each type of
operation (for example, DOWNLOAD for reading and UPLOAD for writing).
Network Topology
The network topology skill provides IP and MAC address location, peer discovery, and route tracing capabilities.
The AI assistant can:
Find which device owns a specific IP or MAC address and where it connects to the network.
List all directly connected peers (neighbors) of a node.
Trace the full network path between any two nodes, showing every hop and intermediate device.
This skill is particularly useful for connectivity troubleshooting, network path analysis, and device location in large networks.
Scheduler Management
The scheduler management skill allows the AI assistant to create, modify, and monitor scheduled tasks.
Supported task types include:
Recurring tasks using cron-style schedule expressions (e.g.,
0 2 * * *for daily at 2:00 AM).One-time tasks with a specific execution time in ISO format, Unix timestamp, or relative notation (e.g.,
+30m).
SSH Command Execution
The SSH skill provides secure remote command execution on servers and network devices monitored by NetXMS. It features an intelligent command classification system that categorizes every command before execution.
Command classification:
Read-only – diagnostic and information-gathering commands that execute immediately without approval. This includes commands such as
ps,df,show interfaces,display version, and most other read-only operations.Write – commands that modify system configuration or state. These require explicit user approval before execution. Examples include service restarts, package management, file modifications, and configuration changes on network devices.
Dangerous – commands that could cause severe damage or data loss (e.g.,
rm -rf /,shutdown,factory-reset). These are always blocked.
Classification is platform-aware and applies device-specific patterns for Linux, Cisco IOS, Cisco NX-OS, Juniper JunOS, Huawei VRP, MikroTik RouterOS, and Extreme EXOS.
Execution modes:
Command channel mode (default for Linux/Unix) – uses the SSH exec channel with full shell processing. Pipes, redirects, environment variables, and command chaining all work correctly.
Interactive mode (automatic for network devices) – handles vendor-specific CLI interfaces with prompt detection, pagination control, and command echo removal.
Approval workflow:
When a write command requires approval, the workflow depends on the session type:
In an interactive chat session, the AI assistant asks the user for confirmation directly in the chat.
In a background task, the AI assistant creates an approval request that the user reviews in the AI Messages panel.
All SSH command executions are logged to an audit table with the timestamp, user, target node, command, classification, approval status, and result.
Function Calling
The AI assistant uses function calling to interact with the NetXMS server in real time. When it determines that it needs live data or wants to perform an action, it invokes one or more registered functions. The results are fed back to the LLM for interpretation. In the management client, function calls appear as progress indicators in the chat, showing what data the AI assistant is accessing (e.g., “Getting alarm list”, “Searching syslog”).
Approval Workflow
For potentially impactful actions, the AI assistant can request user approval before proceeding. This applies to both interactive chat sessions and background tasks.
In interactive chat, the AI assistant presents confirmation dialogs with Approve/Reject, Yes/No, or Confirm/Cancel buttons depending on the context. A configurable timeout ensures conversations are not blocked indefinitely.
In background tasks, the AI assistant sends approval request messages to designated users. The approval request includes a description of the proposed action and spawns a follow-up task if approved.
Background Task Execution Model
Background AI tasks can run multiple iterations, preserving state between executions so the assistant can track progress and compare findings over time.
Object AI Data
AI tasks can store custom key-value data on NetXMS objects using the object AI data storage. This allows tasks to persist findings, baselines, and analysis results directly on the objects they relate to.
For example, a background task monitoring router health could store a performance baseline on each router object and compare against it in subsequent executions.
Reference
Server Configuration
All AI configuration is placed in the netxmsd.conf file.
Global settings
The [AI] section supports the following parameter:
DefaultProviderName of the default provider. If not set, the first provider with the
defaultslot is used automatically.
Provider settings
Each provider is configured in a [AI/Provider/<name>] section.
Parameter |
Type |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
String |
|
Provider type: |
|
String |
(varies) |
API endpoint URL. Defaults to |
|
String |
(varies) |
Model name. Defaults to |
|
String |
(empty) |
API authentication token. Sent as |
|
Float |
-1 |
Sampling temperature (0.0–2.0). Set to -1 to use the provider default. |
|
Float |
-1 |
Nucleus sampling parameter (0.0–1.0). Set to -1 to use the provider default. |
|
Integer |
32768 |
Maximum context window size in tokens. Used by Ollama to set
|
|
Integer |
180 |
HTTP request timeout in seconds. |
|
String |
|
Comma-separated list of slots this provider serves (e.g.,
|
Provider slots
Slots route different types of AI requests to appropriate providers. Assign
one or more slots to each provider using the Slots parameter.
Slot |
Description |
|---|---|
|
General-purpose slot used when no specific slot is requested. At least one provider must be assigned to this slot for the AI subsystem to initialize. |
|
Used for interactive chat sessions with users. |
|
Used for background AI task execution. |
|
Used for deep analysis tasks such as incident investigation. |
|
Used for quick operations where low latency is preferred over capability (e.g., prompt injection guard fallback). |
|
Used by the prompt injection guard. If not defined, the |
Configuration examples
Single cloud provider:
[AI/Provider/openai]
Type = openai
URL = https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions
Model = gpt-4o
Token = sk-your-api-key
Slots = default
Multi-provider setup with slots:
[AI/Provider/claude]
Type = anthropic
Model = claude-sonnet-4-20250514
Token = sk-ant-your-key
Slots = default,analytical
[AI/Provider/ollama-fast]
Type = ollama
Model = mistral
Slots = fast
[AI]
DefaultProvider = claude
Local-only deployment with Ollama:
[AI/Provider/local]
Type = ollama
URL = http://127.0.0.1:11434/api/chat
Model = llama3.2
ContextSize = 32768
Slots = default
nxai Command-Line Reference
nxai [options]
Connection options:
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Server hostname or URL (e.g., |
|
WebAPI port (default: 443 for HTTPS). |
|
Username for authentication. |
|
Password. Prefer using the |
|
Disable SSL certificate verification. |
|
Do not save the session token for reuse. |
|
Clear saved session token and exit. |
Context options (mutually exclusive):
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Bind the chat session to a node by name. |
|
Bind the chat session to an object by ID. |
|
Bind the chat session to an incident. |
Display options:
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Force plain text output (no colors or formatting). |
Environment variables:
Variable |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Default server hostname. |
|
Default username. |
|
Password (avoids passing on command line). |
Session tokens are saved to ~/.config/nxai/sessions.json for automatic
reconnection. Use --clear-session to remove saved tokens.